Through Which Membrane S Would Sodium Chloride Diffuse
In and out of the cell through its plasma membrane. 100 1 rating Sodium chloride diffuses thr.

Resting Membrane Potential Biology For Majors Ii
Salt and other compounds that dissociate into their component ions are called electrolytes.
. Sodium chloride would not pass through any of these membranes. -the potential energy of the solute -the membrane pore size. The solutes can diffuse through the pores.
Through which membranes would sodium chloride diffuse. The solubility of sodium chloride results from its capacity to ionize in water. Experts are tested by Chegg as specialists in their subject area.
Glucose sodium chloride albumin and urea. All cells acquire the molecules and ions they need from their surrounding extracellular fluid ECF. Describe the effect of the dialysis membrane molecular weight cutoff MWCO value on the rate of diffusion.
A specialized example of facilitated transport is water moving across the cell membrane of all cells through protein channels known as aquaporins. The potential energy of the solute. There is an unceasing traffic of molecules and ions.
- Simple Diffusion 8. ByPaul Haney PhD. Up to 24 cash back - Sodium Chloride 6.
Salts such as sodium chloride produce ions when they dissolve in water. Salt transport through dense nonporous polymers occurs via a solution-diffusion process whereby mobile ions sorb into the polymer matrix at the upstream face of the polymer diffuse down a concentration ie chemical potential gradient and desorb at the downstream face of the polymer. Through which membranes would sodium chloride diffuse.
In this activity the solutes were transported through the dialysis membrane by _______. Science Biology QA Library Does sodium chloride dissociate before going through the membrane. For solutes that are membrane permeable which of the following does NOT affect the rate of diffusion.
If you place a salt solution in a container such as dialysis tubing the salt can travel through the very small holes in the tubing. The membrane pore size the potential energy of the solute the. In low bicarbonate media the basolateral membrane chloride conductance is small that is 6 of the basolateral conductance 92.
Which of the following would result in NO change in osmotic pressure across a membrane. In this activity the solutes were transported through the dialysis membrane by _____. Through the use of ion channel proteins and carrier.
Sodium chloride urea glucose albumin. Salts such as sodium chloride are small but in water they split into electrically charged ions and their electrical charge keeps them from penetrating. A teaspoon of table salt readily dissolves in water.
200 MWCO only E. Which of the following statements about carrier proteins is FALSE. Some molecules and ions such as glucose sodium ions and chloride ions are unable to pass through the phospholipid bilayer of cell membranes.
Glucose Na Ca 2. A Revie Which of the following solutes would move the fastest. Albumin glucose urea sodium chloride Submit Request Answer Part B For solutes that move by simple diffusion which of the following does NOT affect the rate of simple diffusion across a membrane.
Sodium chloride glucose albumin. The potential energy of the solute. The glucose diffused through the 200MWCO membrane while there was no diffusion of albumin.
We review their content and use your feedback to keep the quality high. 1 illustrates the steady-state salt flux n s and the simplest possible. View the full answer.
Sodium chloride glucose and albumin generated osmotic pressure. Through which membrane s would sodium chloride diffuse. 8 A 100 MWCO and 200 MWCO B 50 MWCO 100 MWCO and 200 MWCO.
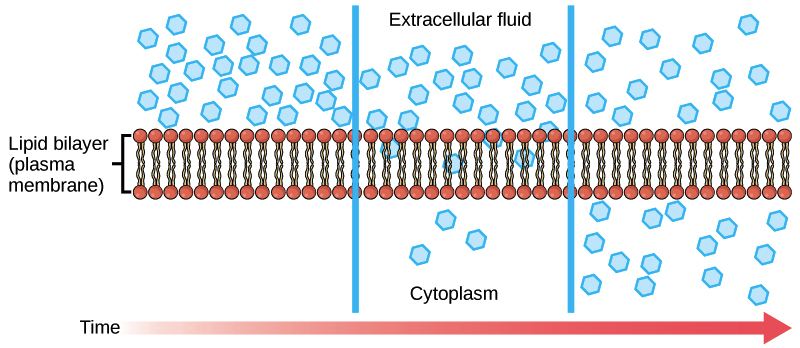
The dotted blue channels represent sodium leak channels. However the membrane is also permeable to chloride and sodium and the flow of these ions keep the resting membrane potential more positive than potassiums equilibrium potential. Through which membranes would sodium chloride diffuse.
50 MWCO 100 MWCO and 200 MWCO. Ions can however pass cellular membranes through channels and transporters. That is why it would require too much energy to dehydrate them and to bring them through the lipid bilayer.
Osmosis is the diffusion of water through a semipermeable membrane from where there is more relative water to where there is less relative water down its water concentration gradient Figure 315. In this activity the solutes were transported through the dialysis membrane by _____. - The Kinetic energy of the Solute 7.
Check all that apply. Dialysis is a classic laboratory technique that relies on selective diffusion of molecules across a semi-permeable membrane to separate molecules based on size. Put the following in order from smallest to largest molecular weight.
Albumin and glucose diffuse through the membrane. The membrane is most permeable to potassium at rest and this leads to potassium efflux. Question 24 of 32 00 30 Points In the laboratory simulation the solutes were transported through the dialysis membrane by _____.
Facilitated diffusion is a type of passive transport that allows substances to cross membranes with the assistance of special transport proteins. In 10 mM HCO 3 1 CO 2 about 50 of the. Transport of Electrolytes across Cell Membranes.
Dialysis is used for a wide variety of applications. The solutes can diffuse through the pores and the concentration of solutes is the same on both sides of the membrane. Who are the experts.
When dialysis tubing containing a solution of salt ions is placed into a beaker of water the ions can diffuse out of the tubing and into. On the other hand NaCl exists as hydrated Na and Cl- ions in solutions that are charged and carry a large hydration shell. In water sodium chloride NaCl dissociates into the sodium ion Na.
In eukaryotic cells there is also transport in and out of membrane-bound intracellular compartments such. For solutes that are membrane permeable which of the following does NOT affect the rate of simple diffusion across a membrane. Desalting buffer exchange removal of labeling.
I am wondering because in semipermeable membranes sodium chloride should be able to pass through but if it dissociates then it would need a transport protein. B The net movement of water is toward the albumin. The mechanism of chloride transport from cell to basolateral solution appears to result from both conductive transport and electroneutral KCl cotransport 19 66.

The Membrane At Rest Foundations Of Neuroscience

Osmosis An Example Of Facilitated Diffusion Nursing School Survival Facilitated Diffusion School Survival

Regular And Facilitated Diffusion Membrane Biology Facilitated Diffusion
No comments for "Through Which Membrane S Would Sodium Chloride Diffuse"
Post a Comment